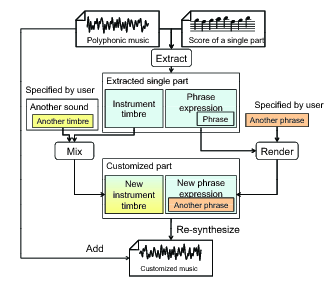
Figure 1: System overview

Figure 1: System overview
Our final goal is to customize an existing musical performance as an user likes. This page presents a new music manipulation method that changes the timbre and phrase of an existing instrument performance in polyphonic sound mixture by incorporating score information of the performance. Changing timbre means to replace instrument type, and changing phrase meand to change the score being played.
The system overview of our approach is shown in Figure 1. Here we define instrument timbre as component that is determined by the musical instrument, which does not change during the performance. Then, the deviated component is defined as phrase expression, which changes mainly according to the musical score. Accordingly, we construct the system with the following three primitive functions;
The resulting changed part is re-mixed with the remaining parts of the original performance to generate a new polyphonic music signals.
To realize such a method, two major requirements must be satisfied. One is to keep expressiveness of the performance during the manipulation as if the new performance is played by the same player. Existing performance generating tools such as MIDI synthesizer ignore original timbre or expression and therefore the synthesized performance is quite different from original performance. The other requirement is to achieve the sound manipulaton even if the source audio signal is polyphonic audio mixture. This is because that most musical pieces consist of several instrument parts and are released usually in stereo.
Changing a EWI (Electronic Wind Instrument) part to a trumpet one and replacing phrase partially.
| Original Sound | |
| Extracted performance | |
| Residual Sound | |
| [Timbre Maniplation] Change to trumpet sound (using trumpet single tone) | |
| [Phrase Maniplation] Create another phrase (using another score) | |
| Remix above manipulation results |
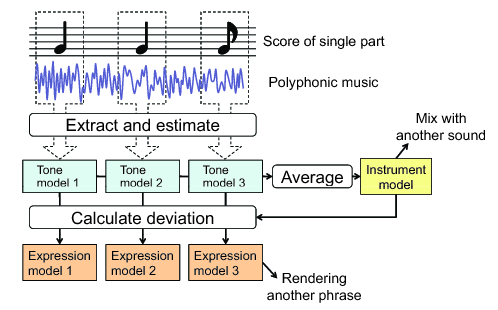
Figure 2: Flowchart based on our approach
Our method is formulated as analysis, manipulation and synthesis of power spectrogram. We define a mathematical musical-tone model that represents each single tone by refering Itoyama's integrated model[1] that is the sum of parametric harmonic-structure model and non-parametric inharmonic-structure model. The extraction of a source part from polyphonic music is then regarded as estimating this model parameters. Instrument timbre is also regarded as the average parameter values of tone models, and phrase expression is regarded as the deviations of the tone-model parameters from the averages. We call this averages instrument model and call this deviations expression model. Mixing and Rendering are impremented as manipulation of instrument model and expression model, respectively. A flowchart based on our approach is shown in Figure 2.
This work contribute to the following applications:
This research was achieved by using RWC Music Database, and was partially supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), the Global Center of Excellence Program (GCOE), and the CrestMuse Project of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST).